
3D printing is a rapidly growing technology with many advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. It however has its problems, including that 3D printing cannot be effectively used for mass production, and is limited in speed and accessibility. Another manufacturing technique for low-to-mid production is CNC machining (computer numerical control), a fairly common subtractive technique for part creation. We decided to compare the advantages and disadvantages for each method to establish where these technologies are most appropriate.
Subtractive vs Additive Manufacturing
|
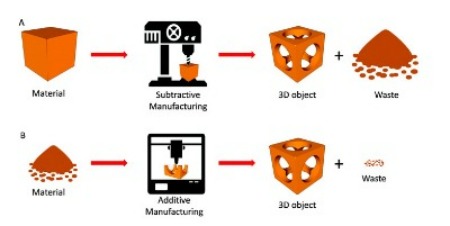
They key difference between 3D printing and CNC machining is that 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing, whilst CNC machining is subtractive. This means CNC machining starts with a block of material (called a blank), and cuts away material to create the finished part. To do this, cutters and spinning tools are used to shape the piece. Some advantages of CNC machining include great dimensional accuracy as well as many compatible materials, including wood, metals and, plastics.
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, involves parts being created layer-by-layer using materials such as plastic filaments (FDM), resins (SLA/DLP), plastic or metal powders (SLS/DMLS/SLM). Using a source of energy such as a laser or heated extruder, layers of these materials are solidified to form the finished part. Advantages of 3D printing include its freedom of shape, applications in many sectors, accuracy, speed, and ability to cut costs and weight in parts. |
 |
Key Similarities of 3D Printing vs. CNC Machining
CNC machining and 3D printing have a few basic things in common:
They make 3D products based on 3D models.
They do so by following instructions from a computer.
They are compatible with STL and OBJ file types.
They are at the forefront of technology.
They are common today.
Beyond these basic similarities, however, CNC machining and 3D printing satisfy largely different demands and offer different benefits.
Key Differences Between 3D Printing and CNC Milling
There are also several major factors that differentiate the two processes.
1. Wastefulness
One of the main differences in additive vs. subtractive manufacturing is the amount of waste they produce. Because CNC machining takes away material, it ends up producing a lot of waste that is impossible to recycle. As you can imagine, the cleanup tends to be messy. 3D printers, however, only use the precise amount of material necessary to produce the part so no cleanup is necessary afterward. 3D printers also produce less noise, as they don’t vibrate during production.
2. File Types
Except for the two file formats mentioned above, CNC machining and 3D printing use file types that aren’t compatible with each other.
3. Size of Parts
With CNC milling, you can make a broad range of different size parts. In 3D printing, on the other hand, the parts you make cannot be any larger than the printing bed. You can produce large components with a 3D printer, but it would involve breaking the component into smaller parts, printing those parts separately and then assembling them. Needless to say, this adds a large amount of time to the production process.
4. Material Availability
CNC manufacturing can work with a wide range of materials, such as metal alloys, wood, acrylics, modeling foam and thermoplastics. 3D printers, in contrast, work with a more limited number of materials, using primarily plastics, metals and polymers. They cannot work with metals with high melting points. In addition to accommodating many materials, CNC machines are also easy to adapt to use new materials. A 3D printer, on the other hand, can only work with one material.
5. Speed
Another key difference between CNC and additive manufacturing is the speed. When it comes to mass-producing a product, CNC machining is faster because it involves an assembly line of machines producing each part. A single 3D printer makes the entire product from start to finish, which makes it less suitable for large-scale production.
6. Production
CNC machining is more precise, providing accuracy to the nearest micrometer. That is because CNC machines have a higher tolerance capability. 3D printing is still far from achieving this level of precision.
7. Repeatability
CNC machines can consistently produce a product the same way each time.
8. Quality
Because of their higher tolerance, CNC machines can produce products with a more polished look. The materials don’t get deformed during manufacturing. Parts made by 3D printers, however, tend to bend and warp, and layer lines can be visible, especially around curves. Although some 3D printers do promise a high degree of accuracy, they still manage to fail at times. Both manufacturing methods have geometric limitations. CNC, for instance, can produce very thin walls, but 3D printing has limitations in this regard, and the size of its end-effector often determines its ability.
What's the best way to manufacture complex parts?
Part complexity is a major factor to consider when choosing between 3D printing and CNC machining. Both technologies have their share of design limitations, though CNC machines can produce far fewer geometries.
CNC machining involves several key design limitations, including tool access and clearances, hold or mount points, as well as the inability to machine square corners due to tool geometry. Some geometries are even impossible to manufacture with CNC, as the tools can’t access all surfaces of your part. This goes for 5-axis systems as well.
Most geometries require the operator to rotate the part so tools can access different sides and angles. Repositioning adds to the processing and labor time, and in some cases, jigs and fixtures are required. All of these factors will raise the final price of the part.
Compared to CNC, 3D printing can produce parts with very few geometric limitations. Support structures may be needed for processes like FDM, but a little extra post-processing doesn’t diminish the vast design freedom and capacity for complexity you get with 3D printing.
Plus, polymer-based powder bed fusion processes such as SLS and MJF can produce freeform, organic geometries without the need for support structures. The ability to produce highly complex geometries with relative ease is one of 3D printing’s key strengths.
Top tips & tricks for choosing between 3D printing & CNC machining
Selecting the right manufacturing technology for your custom parts may feel like an insurmountable challenge, but it doesn't have to. We’ve put together a few essential rules of thumb to follow if you’re facing this decision.
Choose CNC machining if you are producing parts in medium to high quantities (250-500 parts) that have relatively simple geometries
Choose 3D printing for lower quantities of parts—or single prototypes—and if your designs have complex geometries
When considering metals, CNC can be price competitive even for low quantities, but geometry limitations still apply
If you’re printing more than 500 parts or so, maybe consider other technologies like injection molding (or a mix of 3DP or CNC and a forming process)
Do you think of making use of one of the two processes in your project? Why not try us at GT? GT specialized in CNC machining and 3D printing for 13 years ,Which is a high quality CNC machining service provider in China,Provide high quality 5 - axis processing services and 3D printing services. Our expert team is highly knowledgeable in CNC machining and 3D printing, and we can guarantee high-quality products tailored to your requirements. Get in touch with a member of the GT team or upload a quote via the link below. We’re at your service!